gcsescience.com 19 gcsescience.com
What happens to the Voltage
and Current
in a Circuit when Cells are connected in Series?
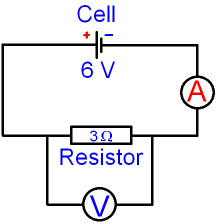
The current
in the circuit below can be calculated
using the equation
voltage = current x
resistance V = I x R
The equation
can be rearranged to give
current
= voltage
÷ resistance
I =
V
÷ R

In the circuit above, V = 6 volts and R = 3 ohms.
I =
V
÷ R
= 6 ÷ 3
= 2 amps.
What happens to the Voltage
and Current
in a Circuit if Two Cells are connected in Series?
If an identical cell
is
placed in series
with
the original
cell, the current in the circuit doubles
because the total voltage of the circuit doubles.

In the circuit above,
R = 3
ohms and V
= 6 + 6 volts = 12 volts.
I =
V
÷ R
= 12 ÷ 3
= 4 amps.
Cells connected together
are called a battery.
If more cells (or batteries)
are connected together
in series then the total
supply voltage is the
sum of the individual
voltages for each cell if they are
connected the right way round, plus
to minus.
Compare this with cells in parallel.
![]() Links
Electricity
Series Circuits
Revision Questions
Links
Electricity
Series Circuits
Revision Questions
![]()
gcsescience.com Physics Quiz Index Electricity Quiz gcsescience.com
Home GCSE Chemistry GCSE Physics
Copyright © 2015 gcsescience.com. All Rights Reserved.