gcsescience.com 4 gcsescience.com
What is Electric Current?
Current is
the "rate of flow of coulombs"
in
an
electric circuit. A coulomb
is a unit of charge,
so an electric
current is a flow of charge.
Charge is given the symbol
Q.
Current is given the symbol I.
This is the capital letter I, not a number 1.
Current is measured in amps.
What is an
Amp?
1 amp = 1 coulomb per second.
The word "per" means "divided
by",
so current = charge
÷
time. I = Q
÷ t.
We can calculate the current
if we know
the charge and the time.
This equation
can be
rearranged to give
charge = current x time.
Q = I x
t.
Current
can also be calculated using
I = P
÷ V and I =
V
÷ R
See all equations for electricity.
How is Current measured?
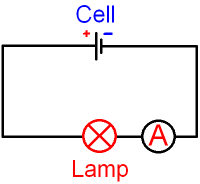
Current is measured using an ammeter.

The circuit diagram above shows how to measure
the
current flowing through a lamp.
The circuit symbol
for an ammeter is a circle with the letter
A inside. An
ammeter is always connected in series with a component.
If the ammeter reads 1 amp,
then the current (I) = 1 amp at that
point in the circuit.
I = 1 amp
= 1 coulomb per second.
If the ammeter reads 6 amps,
then I = 6 amps = 6
coulombs per
second.
Current
has a heating
effect
and thick
wire must be used to carry a large current.
![]() Links
Electricity
Revision Questions
Links
Electricity
Revision Questions
![]()
gcsescience.com Physics Quiz Index Electricity Quiz gcsescience.com
Home GCSE Chemistry GCSE Physics
Copyright © 2015 gcsescience.com. All Rights Reserved.