gcsescience.com 3 gcsescience.com
What is a Coulomb?
A coulomb is a unit of electrical
charge.
Charge is given the symbol
Q.
Electrons
are tiny and have a very small
charge.
In the physics
of electricity, we take a
very
large number of electrons as 1 unit of charge
called a coulomb.
1 coulomb = 6·2 x 1018 electrons.
This is 6·2 million million million
electrons.
Such a large number of electrons
can do useful
things like light a lamp.
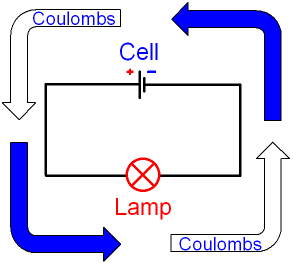
What is Direct Current?
There are two different
types of power supply.
One type supplies alternating current
and the other type supplies direct current.
A cell or a
battery supplies direct
current.
With direct current,
electrons
leave from one side of
the cell, pass through
all of the components in
the circuit and return back to the other side of the cell.
The electrons are given
energy by the power
supply
and they then transfer
this energy to all of the
components
in the circuit. Electrons are not
used up
by the
components. The same number of electrons
leave from one side of the cell and return to the
other.

What do we need to know about Coulombs?
We need to know
1. The rate of coulombs
flowing in the
circuit.
The number of coulombs per
second is called the
current.
2. How much energy each coulomb has.
The number of joules per
coulomb is called the
voltage.
![]() Links
Electricity
Revision Questions
Links
Electricity
Revision Questions
![]()
gcsescience.com Physics Quiz Index Electricity Quiz gcsescience.com
Home GCSE Chemistry GCSE Physics
Copyright © 2015 gcsescience.com. All Rights Reserved.