gcsescience.com 8 gcsescience.com
What is Resistance?
Resistance is a measure of how much a component
decreases the current (see resistor).
The bigger the resistance, the smaller the current.
Resistance
is measured in ohms (symbol Ω).
See how to calculate
the resistance of a component.
What is Ohm's Law?
The very important equation
voltage = current x resistance V = I x R
is an expression of ohm's law.
If the
resistance of a component is
constant (constant
means it stays
the same) then
a plot (graph) of
current against voltage
will be a straight line. The
gradient
(slope) of the line
shows how big the resistance
is.
A test circuit is used to find
how the current through a
component changes as the voltage
changes.
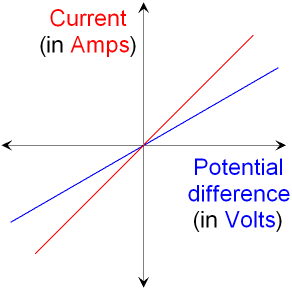
Below is a plot for two components that obey
ohm's
law.
The component with the blue
line shows a smaller
current flowing and therefore has a bigger
resistance.

Wires and resistors are examples of components that
obey
ohm's
law. To be precise, a component
will only obey ohm's law at constant temperature.
In reality, an increase
in current through
a component will
increase its temperature
and
so ohm's law is only an
approximation
but it works quite well for many
components.
See the theory
of electrical resistance.
Diodes,
lamps and thermistors
are
examples of components that do not obey ohm's
law.
![]() Links
Electricity
Resistance
Revision Questions
Links
Electricity
Resistance
Revision Questions
![]()
gcsescience.com Physics Quiz Index Electricity Quiz gcsescience.com
Home GCSE Chemistry GCSE Physics
Copyright © 2015 gcsescience.com. All Rights Reserved.