gcsescience.com 7 gcsescience.com
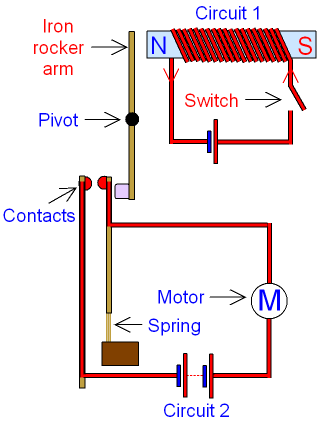
How does a Relay Work?
The relay consists of two
circuits. Circuit
1 is a
simple electromagnet which requires only a small
current.
When the switch is closed, current
flows
and the iron rocker arm is
attracted to the electromagnet.
The arm rotates about the central
pivot and pushes
the
contacts together.
Circuit 2 is now switched on.

Circuit
2 may have a large current
flowing through it,
to operate a powerful motor or very bright lights.
When the switch is opened the
electromagnet releases
the
rocker arm
and the spring moves the contacts apart.
Circuit 2 is now switched off.
Why is a Relay Used?
The advantage of using a relay is that a
small
current (circuit
1) can be used to
switch on and off a
circuit with a large current (circuit
2).
This is useful for two
reasons.
1. The low current
circuit (circuit 1) may contain a
component
such as an LDR, which only uses small currents.
2. Only the high current
circuit (circuit 2)
needs to be made from thick wire.
A relay is used to operate the starter motor in cars
and the heating circuit in
diesel engines.
![]() Links
Electromagnetism
Revision Questions
Links
Electromagnetism
Revision Questions
![]()
gcsescience.com Physics Quiz Index Electromagnetism Quiz gcsescience.com
Home GCSE Chemistry GCSE Physics
Copyright © 2015 gcsescience.com. All Rights Reserved.