gcsescience.com 12 gcsescience.com
What is an Electric Motor?
An electric motor
is a device
that
transfers
electrical energy into rotational energy.
Something that spins round has
rotational energy.
Rotational energy is a form of
kinetic
energy.
Electric motors have a wide variety of uses.
How does a Simple Electric Motor Work?
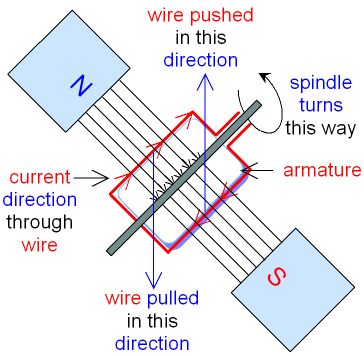
The catapult effect
(motor effect) is used to
make a
simple electric motor spin round.
The wire is pushed in the opposite direction
if the direction of the current through it is reversed.
In a motor, the wire is
wound around a central block
called an
armature.
A spindle through the armature allows it to rotate.
The current flows in opposite directions
on each side
of the armature, so one side is pushed while
the other is pulled.
This makes the armature rotate.

After the armature has rotated
through half a turn (180°),
then the side of the armature being pushed
upwards
in the above picture is now on the left
and the
side being pulled down on the right. The
armature would be trying to turn
in the opposite direction.
For the armature to continue
to spin in the same direction,
the direction of the current flowing through the wire
must be reversed every half
turn. This is achieved
using a split - ring
commutator (see the next page).
![]() Links
Electromagnetism
Revision Questions
Links
Electromagnetism
Revision Questions
![]()
gcsescience.com Physics Quiz Index Electric Motor Quiz gcsescience.com
Home GCSE Chemistry GCSE Physics
Copyright © 2015 gcsescience.com. All Rights Reserved.