gcsescience.com 3 gcsescience.com
Igneous Rocks and the Structure of the Earth.
The Earth is about 4·6 billion
years old (4,600,000,000 years).
In the beginning, the Earth was very hot
and molten (liquid).
The Earth cooled, and about 4 billion years
ago it had cooled
enough for the first solid rock
crust to form on the surface.
This first solid crust was made from the first
igneous rocks
that had formed on the surface of molten
magma.
What is Magma?
Magma is a thick
liquid molten rock that can form within
the mantle or the crust as a result of tectonic
activity.
The mantle mainly contains hot
solid rock which can flow
only very very
slowly. This slow movement makes
sections (plates) of
the crust collide
or slide past each other.
The enormous amount of energy which is released when
plates collide is sufficient to melt parts of the mantle or crust
and
form magma. The magma can then
cool and
become solid inside the crust (see the formation
of granite)
or flow from a volcano and become solid
on the
surface of the crust (see the formation
of basalt).
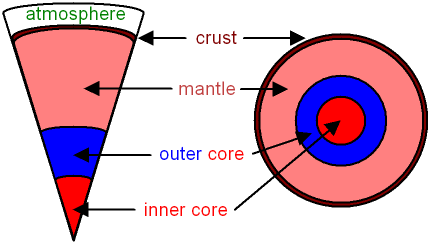
The structure of the Earth is shown in the picture below.

At the centre of the Earth
is the core, which is made
from mainly iron and nickel.
In the middle (called the inner
core) it is solid.
Further out (the outer core) it is liquid.
The outer core is between the inner core and the
mantle.
Waves from earthquakes
give us
information about the structure
of the Earth.
The oldest rocks are
igneous rocks.
They are called igneous from the
Latin ignis, meaning fire,
like ignite - set fire to.
The Earth's crust, oceans and atmosphere
are the sources
of all raw materials from
which everything we see around us is
made.
![]() Links Igneous
Rocks Revision Questions
Links Igneous
Rocks Revision Questions ![]()
gcsescience.com The Periodic Table Index Rocks Quiz gcsescience.com
Home GCSE Chemistry GCSE Physics
Copyright © 2015 gcsescience.com. All Rights Reserved.