gcsescience.com 27 gcsescience.com
Ray Diagrams for Images made by a Convex Lens.
The type of image
made by a convex lens
depends on how far away the object
is.
The first picture below shows how to draw a ray
diagram
for an object that is further
away from the lens than 2F.
Further down the page there is a picture showing
a ray
diagram for an object
that is between
F and 2F.
Click
here for a ray diagram for
an object that is nearer
the lens than F.
F is at the focal
point of the lens.
The distance from F to the centre of
the lens is the focal
length.
2F
is twice the focal length.
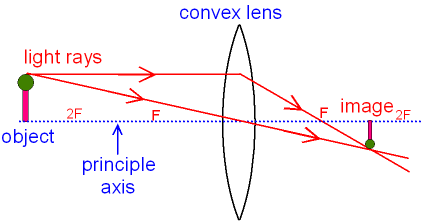
Ray
diagram for an object
that is
further
away from the lens than 2F.
The bottom of the object
is placed on the principle axis.
Two rays of
light are
drawn from the top of the object.
The first ray of light
is parallel to
the principle axis
and therefore
passes through the focal
point.
The second ray of light
goes from the top of the object
and passes straight through the centre
of the lens.

The top of the image
is formed where the two rays of light
cross.
The bottom of the image
is still on the principle axis.
You can see that the image
is not the same as the
object.
The image is smaller
than the object.
The image is real
meaning that the
light rays really go
there
(compare this with virtual).
The image is inverted (meaning
it
is upside down).
The next picture shows a ray
diagram
for an object that is between
F and 2F.
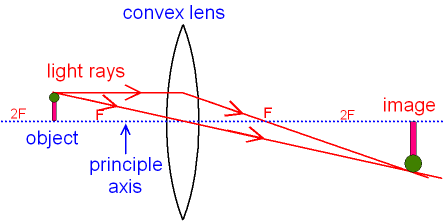
As above, you can see that the image
is
not the same as the
object. The image is still real
and inverted but it is now bigger
than the object.
![]() Links
Waves
Light
Revision Questions
Links
Waves
Light
Revision Questions
![]()
gcsescience.com Physics Quiz Index Lens Quiz gcsescience.com
Home GCSE Chemistry GCSE Physics
Copyright © 2015 gcsescience.com. All Rights Reserved.